Updating Our SEO Strategy: Money Keywords
Money keyword resources on this page:
Getting your SEO strategy right can be the difference between projecting your audience reach into the thousands (or if you’re lucky, millions!), or being virtually invisible.
SEO can make a big impact on driving pipeline and inbound requests - when done right.
This is the story of how we implemented a new content strategy at Cognism after our growth advisor, Gaetano DiNardi, introduced us to the idea. We call it ‘the money keywords strategy’.
Never fear, we’re going to explain - just keep reading! 👇
Our SEO strategy before money keywords
Before January 2023, our SEO strategy was very traditional. The priority was to increase brand awareness and attract quality traffic, so we focused on developing keyword clusters.
We’d do research and find keywords with either high monthly search volume or high intent and conversion potential. Then, we’d create content clusters based on relevant, long-tail keywords.
Monika Kisielewska was the SEO and Content Manager who spearheaded this strategy. She said:
“While we had some transactional keywords in our clusters, we never really focused on them. At the time, we weren’t looking at keywords for conversion.”
“We would usually just build topical clusters around big keywords like prospecting or lead generation. Things that were relevant to the business.”
This SEO strategy was successful for a while; we saw our page rankings shoot to the top positions, and we generated a lot of traffic.
So what was the problem?
People weren’t often taking action once they landed on our pages. Consequently, our conversions were low.
Gaetano said:
“Most software companies fall into the trap of targeting high-volume keywords because they align with the company’s product category. But rarely do they produce new customer acquisition.”
Monika added:
“It reached a point where we had too many pages to manage. It was hard to update decaying content while producing new content.”
“And we felt we were missing out on valuable competitor traffic - by not optimising competitor pages for search engines.”
Because we’re in a well-established industry, we don’t need to focus as much on educational content, such as ‘What is lead generation?’
Instead, we decided to focus on the terms that would bring more potential customers to our site. Our goal was to create content that converted.
Enter money keywords!
What is the money keyword strategy?
Fundamentally, the money keyword strategy is about targeting keywords that high-intent buyers use to find solutions to their problems.
Gaetano said:
“If we had a roulette wheel in front of us and we were betting on the board, which keyword do we think represents the most traffic that is the most likely to be in-market?”
In other words, it’s about focusing on the quality of the traffic rather than the volume. This is an essential part of our enterprise content marketing strategy, which helps us capture demand.
The thinking goes like this:
It’s better to spend more time and money driving smaller volumes of high-converting traffic to your site than driving as much traffic as possible and having next to zero people take any action.
So, what is a money keyword exactly, and how do you decide which keywords to use?
It’s about finding keywords that balance:
- What in-market buyers are searching for.
- The business potential of the topic.
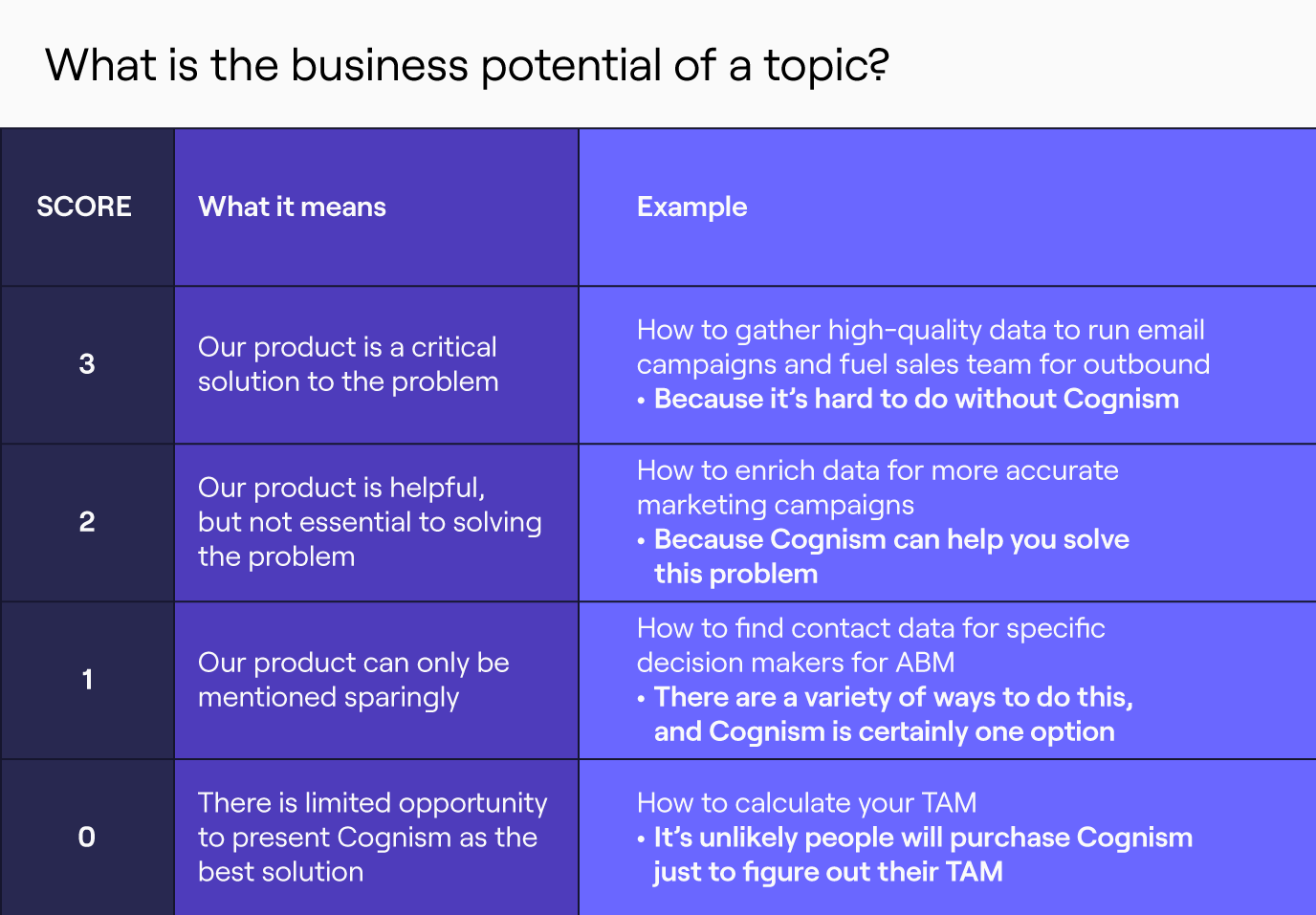
Our money keywords had to fit in that score 3 category.
These keywords positioned Cognism as a critical solution to the problem, for example: ‘how to gather high-quality data to run email campaigns and fuel sales teams for outbound’ or ‘B2B data contact provider’.
These keyword ideas are valuable because it’s highly likely that someone searching for them is very close to considering a solution like ours.
This is in contrast to the old way of SEO. Before, we focused on search terms like ‘how to do demand generation’ or ‘how to calculate your TAM’. These phrases have high search volumes, so loads of people will find your website that way, which isn’t a bad thing. But the crucial thing is they’re unlikely to convert off the back of that search.
Monika said:
“Think of it as a growth strategy. Once you have the money keywords list and you rank for your target keywords, you need to think about what you’re doing with this traffic.”
“Do you give users a chance to convert? Can you optimise your page for that?”
“We’re now looking at our blog template, live chat messaging, CTA placement, and other factors that don’t impact SEO rankings but can impact that page’s success.”
How to implement a money keyword strategy
What are the steps for implementing a strategy like this?
We took the following steps 👇
1. Deeply understand the product
We had to answer the following questions:
- What does our product do?
- What is it good/bad at?
- What are the benefits of using it?
- How does it compare to what our competitors offer?
Monika said:
“Money keywords belong to the category where you have to position your product as a solution to the customer’s problem.”
“This means you need to understand the product really well to provide the right information. We have to help them realise that our solution is the one they need.”
We created and updated our competitor pages using information about our product and our competitors’ products. This included listicle blog posts that mentioned our competitors, such as this page on ZoomInfo alternatives.
We also capitalised on traffic searching for our competitors. For example, when a prospective buyer searches for Lusha or ZoomInfo as a solution for their data needs, we can piggyback off those search terms.
Check out these pages we published targeting the Lusha vs ZoomInfo and ZoomInfo pricing keywords. These pages compare our competitors’ features, pricing, data and more, while positioning Cognism as the solution they should consider.
This technique is known as ‘crash the party’ SEO.
2. Analyse our existing keywords and identify new opportunities
For this, we used GSC and Ahrefs. Where did we rank for which keywords, and how far off were we from the desired end state?
Armed with this information, we got to work filling in the gaps with the new money keywords we had identified. For example:
3. Follow rules for creating money keyword content
Our money keyword pages are a mix of newly published and updated blogs.
Here, we gave ourselves some more rules to follow 👇
- If the existing content generates high traffic but few conversions, then we optimise for conversions.
- If the existing content generates lots of conversions but little traffic, then we optimise for search.
- To optimise for conversions, our goal is to make better use of case studies in our content - they have above-average conversion rates but generate relatively little traffic.
Monika said:
“The hardest part of implementing this strategy is to learn and deeply understand your product and how it’s better or different from your competitors. This knowledge helps you produce relevant content.”
“You need to really understand what prospects might be looking for, the specific language they use when searching.”
“Equally tricky is to talk about Cognism and its competitors, positioning it as the right purchasing decision without making any statements that unintentionally bash our competitors or mislead prospective buyers.”
“To ensure we don’t overstep the mark, we have our pages reviewed by our product and legal teams.”
How to track a money keywords strategy
Traditionally, we tracked SEO metrics like:
- Organic traffic growth.
- Number of keywords in top positions.
But under this new strategy, our tracking looks a little more sophisticated.
Traditional SEO metrics are joined with a new emphasis on measuring conversions.
We’re currently tracking:
- Direct conversions.
- Assisted conversions.
- Organic traffic growth.
- Number of keywords in top positions.
We were able to tie organic traffic back to revenue by leveraging HockeyStack, one of the top marketing attribution tools on the market.
While this strategy is in its early days - we only started working on money keywords at the beginning of Q1 2023 - we’ve already seen very promising results.
For example, we had a record-high number of conversions from blog pages - 16% higher in Q1 versus Q4 last year!
Plus, our organic traffic increased by 22.38% from January 2023 to now. Our traffic value rose by a similar amount, 22.12%.
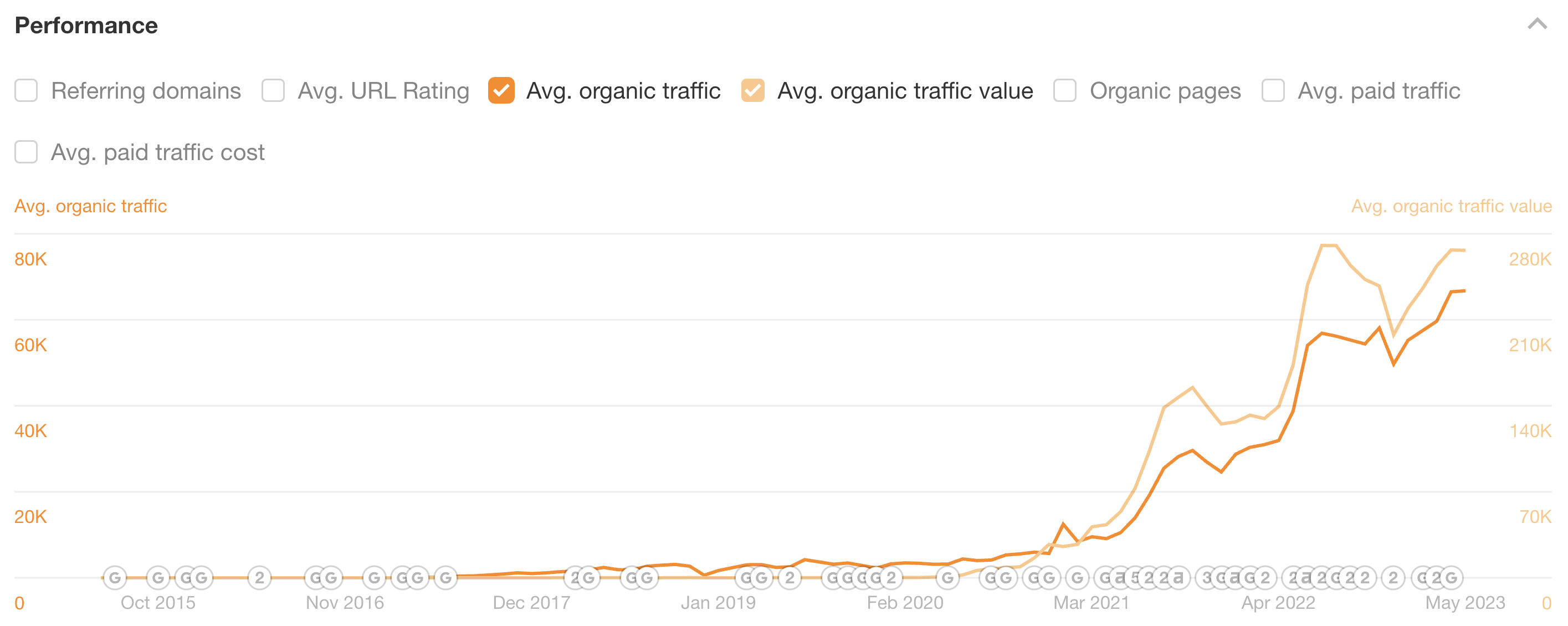
We also registered record blog views in Q1 as we rolled out the money keyword strategy.
Money keywords: the last word
To bring this SEO strategy deep dive to a close, we’ll leave you with some parting advice from Monika:
“Learn about your product. Speak to stakeholders about it. Listen to customer calls and understand the language they use. Then just get started - you can always iterate and fine-tune later.”
“If you’re in a well-established category where your competitors have well-known brands, don’t be afraid to use their branded traffic for your benefit.”
“If there’s something customers don’t like about your competitor, and you solve that pain point, add it to your money keyword list.”
“For example, ‘[competitor name] pricing’ - describe their pricing to fulfil organic search intent but show how yours provides better value.”